Recycling Lives Services: A Full Option for Corporate Recycling
Recycling Lives Services: A Full Option for Corporate Recycling
Blog Article
Checking Out Various Kinds of Waste in Modern Waste Monitoring Solution
The contemporary landscape of waste monitoring entails navigating a complicated variety of waste types, each requiring specialized handling and disposal approaches to mitigate ecological effects. Municipal strong waste, harmful waste, electronic waste, and organic waste each present distinctive difficulties and chances for source recovery.
Metropolitan Solid Waste
Municipal strong waste, usually described as family trash or garbage, incorporates a range of disposed of materials created by property, commercial, and institutional sources within a community. This waste stream commonly includes items such as packaging, food scraps, backyard trimmings, paper, plastics, textiles, and thrown out family products. The administration of community strong waste is an important component of urban preparation and public health and wellness, necessitating reliable collection, transportation, and disposal systems.
Efficient waste monitoring systems are made to decrease environmental influence while maximizing source healing. Composting natural waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, not just minimizes landfill use yet also generates valuable soil changes.
Districts need to also attend to the economic and logistical difficulties linked with waste management. Executing pay-as-you-throw systems, enhancing public recognition, and investing in innovation can dramatically boost waste diversion prices. By incorporating these techniques, towns can foster lasting areas, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and conserve natural sources.
Contaminated Materials
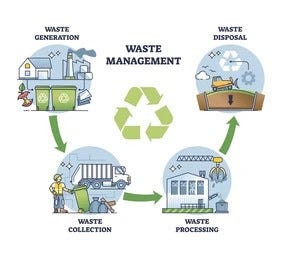
Effective contaminated materials monitoring entails numerous critical steps: recognition, disposal, partition, and therapy. Recognition entails the category of waste based upon its unsafe properties. Segregation ensures that unsafe materials are saved individually from non-hazardous waste to avoid cross-contamination. Therapy methods, such as chemical neutralization, incineration, and stabilization, are employed to decrease the poisoning, quantity, or mobility of the waste. Disposal alternatives, including protected land fills and below ground storage, are chosen to make certain long-lasting control.
Governing structures, such as the Source Preservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States, supply standards and standards for dangerous waste administration. Adherence to these policies, combined with advancements in waste treatment modern technologies, is vital in minimizing the dangers related to contaminated materials.
Electronic Waste
Electronic waste, generally described as e-waste, stands for a rapidly growing challenge in waste administration systems globally. This type of waste incorporates disposed of digital gadgets and tools such as smartphones, computers, tvs, and various other electronic home appliances. The fast rate of technological improvement, combined with decreasing product life expectancies and consumer need for the latest tools, has tremendously boosted the volume of e-waste generated yearly.
E-waste is specifically troublesome because of its complex structure, frequently consisting of harmful materials like cadmium, lead, and mercury, which pose substantial ecological and wellness threats otherwise appropriately handled. Alternatively, e-waste additionally includes valuable materials such as silver, copper, and gold, which can be recuperated and recycled. The dual nature of e-waste-- both useful and harmful-- demands specific handling, recycling, and disposal procedures.
Efficient e-waste management includes strict regulative web frameworks, robust collection systems, and progressed recycling modern technologies. Public awareness and participation are essential, as inappropriate disposal practices, such as prohibited disposing and casual recycling, aggravate environmental contamination and wellness risks. Subsequently, boosting e-waste monitoring methods is vital for minimizing eco-friendly impact and recovering important resources in a progressively electronic world.

Organic Waste
Organic waste, consisting of cooking area scraps, lawn trimmings, and farming deposits, stands for a considerable portion of the worldwide waste stream. This kind of waste is biodegradable, meaning it can be broken down by microbes into simpler organic substances. Regardless of its possibility for all-natural disintegration, inappropriate administration of natural waste can lead to unfavorable ecological influences, including the exhaust of greenhouse gases such as methane, which add to climate adjustment.
Efficient monitoring of organic waste is essential for minimizing these ecological effects (recycling lives services). Composting is an extensively embraced method, changing organic waste into nutrient-rich compost that can improve dirt health and agricultural performance. Furthermore, anaerobic food digestion is an arising modern technology that transforms organic waste into biogas, a renewable power source, and digestate, which can be utilized as fertilizer
Municipalities and waste monitoring entities need to carry out durable organic waste collection and treatment programs to take full advantage of the advantages of these procedures. Public education and learning projects can also play a critical role in motivating houses and services to different organic waste from other sorts of waste. By prioritizing the my blog monitoring of natural waste, societies can reduce land fill use, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and produce beneficial results for farming usage.

Innovative Waste Management
In the realm of waste management, ingenious methods are pop over here changing exactly how cultures handle their refuse, going for sustainability and performance. These innovations incorporate a series of modern technologies and techniques that improve recycling rates, reduce landfill dependency, and lower ecological impact. One famous development is the execution of clever waste bins equipped with sensing units that keep track of fill levels and optimize collection courses. This not only minimizes gas intake yet likewise minimizes greenhouse gas emissions.
One more noteworthy development is the adoption of waste-to-energy (WtE) modern technologies. By transforming non-recyclable waste right into useful power with procedures such as incineration and anaerobic food digestion, WtE minimizes landfill problem and gives an eco-friendly energy resource. In addition, innovations in chemical reusing permit the breakdown of intricate plastics into their original monomers, making it possible for the creation of brand-new, high-grade plastic products.
Furthermore, the circular economy design is getting grip, emphasizing the design of items and systems that prioritize reusability and source effectiveness. This all natural strategy encourages markets to lessen waste generation from the start. With these innovative strategies, contemporary waste monitoring systems are not only resolving the immediate challenges of waste disposal but additionally paving the method for a much more lasting future.
Verdict
A comprehensive understanding of metropolitan strong waste, harmful waste, electronic waste, and natural waste, combined with the execution of innovative waste management options, is necessary for mitigating ecological impacts. Integrating innovations such as smart waste bins and waste-to-energy systems can improve performance and sustainability. Reliable waste administration techniques not just foster source healing yet also advertise public recognition and engagement, inevitably adding to the growth of a round economic situation.
The modern landscape of waste administration includes browsing a complex selection of waste types, each requiring specialized handling and disposal techniques to reduce environmental impacts. Local solid waste, harmful waste, electronic waste, and natural waste each existing unique difficulties and chances for resource recovery.Digital waste, generally referred to as e-waste, stands for a quickly growing challenge in waste management systems around the world. Via these innovative approaches, modern-day waste administration systems are not just resolving the prompt difficulties of waste disposal but likewise leading the means for an extra lasting future.
An extensive understanding of community strong waste, dangerous waste, electronic waste, and organic waste, coupled with the execution of ingenious waste management services, is essential for mitigating ecological effects. (recycling lives services)
Report this page